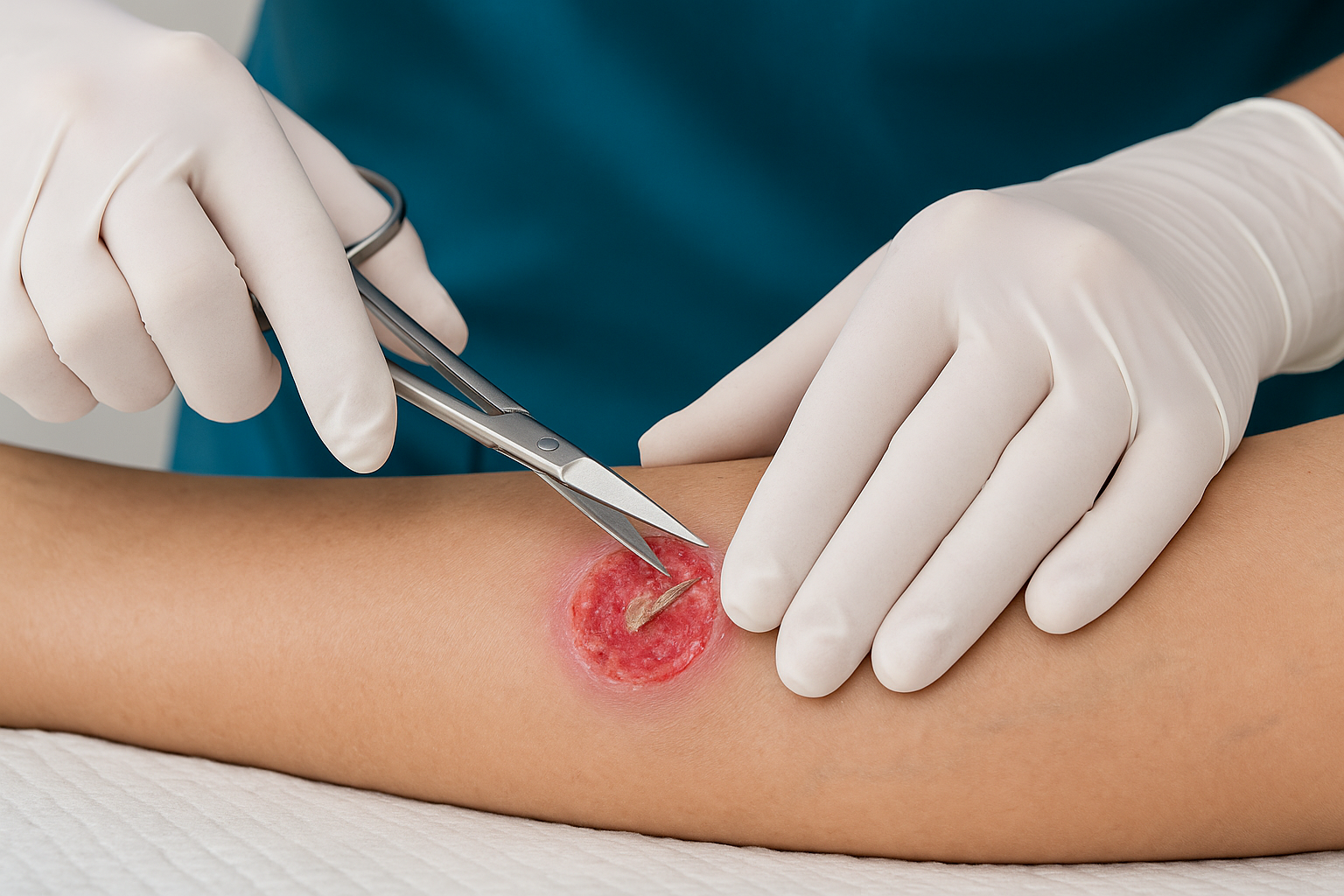
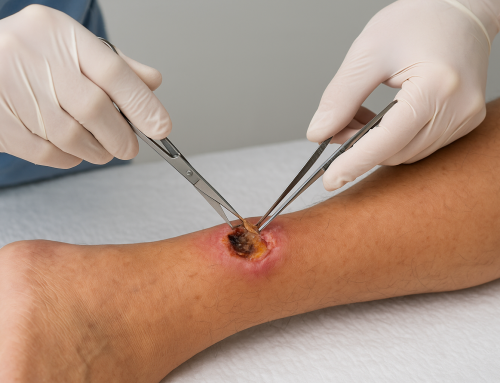
What is Sharp Debridement?
Sharp debridement is a medical procedure used to remove dead, damaged, or infected tissue from a wound using sterile instruments such as scalpels, scissors, or curettes. This method is essential in wound care because it promotes healing by getting rid of tissue that can harbor bacteria and delay recovery.
Why is Sharp Debridement Important?
When a wound has necrotic (dead) tissue, it creates an environment where bacteria can thrive, increasing the risk of infection. Sharp debridement helps by:
- Removing unhealthy tissue quickly and precisely.
- Reducing bacterial load in the wound.
- Stimulating the body’s natural healing processes.
- Allowing healthcare providers to better assess the wound condition.
Types of Wounds Treated with Sharp Debridement
Sharp debridement is commonly used for several types of wounds, including:
- Chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers.
- Pressure ulcers (bedsores).
- Burn wounds.
- Infected surgical wounds.
- Traumatic wounds with dead tissue present.
The Sharp Debridement Procedure Explained
Typically, sharp debridement is performed by trained healthcare professionals in a clinical setting. Here’s a general overview of the steps involved:
- Preparation: The area around the wound is cleaned and often numbed with a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort.
- Debridement: Using a scalpel or scissors, the clinician carefully cuts away dead tissue and eschar until healthy, bleeding tissue is revealed.
- Post-debridement care: The wound is cleaned again and dressed appropriately to support healing.
Depending on the wound size and patient comfort, multiple sessions might be needed.
Benefits of Sharp Debridement
Sharp debridement offers several advantages compared to other debridement methods such as mechanical, enzymatic, or autolytic approaches:
- Speed: It removes dead tissue quickly, often in one session.
- Precision: Allows targeted removal of only necrotic tissue, leaving healthy tissue intact.
- Improved wound bed: Creates an optimal environment for healing and possible skin grafting.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While sharp debridement is highly effective, some risks and considerations include:
- Pain: Some discomfort is expected, which is why local anesthesia is often used.
- Bleeding: Because the procedure exposes healthy tissue, bleeding may occur, particularly in patients with clotting disorders.
- Infection: If performed under non-sterile conditions, there is a risk of introducing infection.
- Not suitable for all wounds: Some wounds with poor blood supply or in certain patients might require different approaches.
It is critical that sharp debridement is conducted by skilled healthcare professionals who can assess when it is appropriate.
Aftercare and Healing Following Sharp Debridement
Post-procedure care plays a vital role in successful healing after sharp debridement. Recommendations include:
- Keeping the wound clean and moist using proper dressings.
- Monitoring for signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Following prescribed antibiotics if given.
- Maintaining adequate nutrition to support tissue repair.
- Regular follow-up with the healthcare provider to check healing progress.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
If you have a chronic wound or one that is not healing, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider. They can evaluate the wound and determine if sharp debridement or another method is appropriate. Early and proper wound management helps avoid complications like infections and non-healing ulcers.
Conclusion
Sharp debridement is a valuable and effective technique in wound care, offering quick removal of dead tissue to promote faster healing. When done correctly, it reduces infection risks and supports better outcomes for patients with various wounds. If you’re dealing with a stubborn or chronic wound, discussing sharp debridement with your healthcare provider could be a key step toward recovery.